Surgery cannot remove the tumor? This set of "combination fists" makes tumors "nowhere to hide"
When it comes to liver cancer, people are very afraid.
More than half of the global liver cancer patients are in China.
In terms of treatment, surgical resection is the first choice, but not all liver cancer can be surgically removed.
What should I do if I cannot remove it? To learn about a "black technology" for treating liver cancer
Tumor size cannot be treated with surgical intervention, showing skill
Mr. Du, 66 years old, sought medical attention at a local hospital due to upper abdominal pain. After examination, it was found that there was a mass in the right lobe of the liver, measuring 6.2 cm x 4.4 cm. The tumor marker AFP was elevated (36.7 ng/ml), and he had a history of hepatitis B. The liver biopsy pathology showed hepatocellular carcinoma. Due to the large size and poor growth location of the tumor, recommended by the local hospital, I came to the Minimally Invasive Interventional Department of Henan Cancer Hospital to seek further treatment.
Dr. Zheng Lin, the chief physician of the Minimally Invasive Intervention Department, received Mr. Du. After multidisciplinary consultations, the expert group believed that the patient had a tumor diameter greater than 5 cm and belonged to large liver cancer. The clinical staging of liver cancer in China is stage 1b. Although Mr. Du has a single tumor, the inner edge of the tumor is adjacent to the inferior vena cava. Experts evaluate that direct surgical resection cannot guarantee an effective surgical margin on the inner side of the tumor and cannot be used as the preferred method.
Zheng Lin analyzed that the patient’s liver tumor has a relatively rich blood supply, which can be used for interventional embolization to reduce the active area of the tumor. Subsequent combined radiofrequency ablation treatment can achieve curative effect for the patient. After consultation from multiple disciplines, Zheng Lin’s medical team has decided to perform drug loaded microsphere embolization and sequential radiofrequency ablation treatment for Mr. Du.
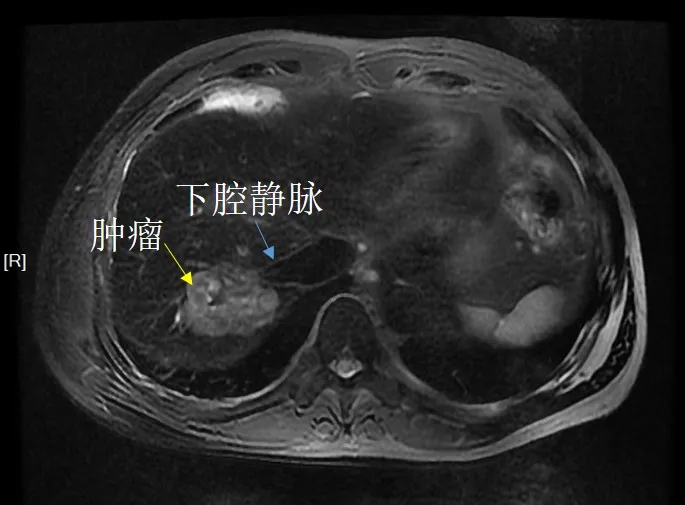
Before treatment, Mr. Du’s tumor was located near the inferior vena cava (as shown in the above picture)
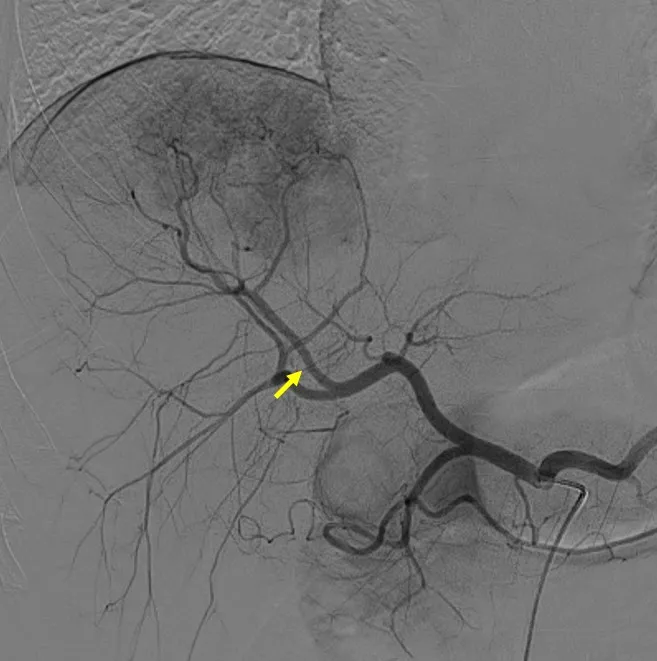
Tumor blood supply artery (indicated by yellow arrow)
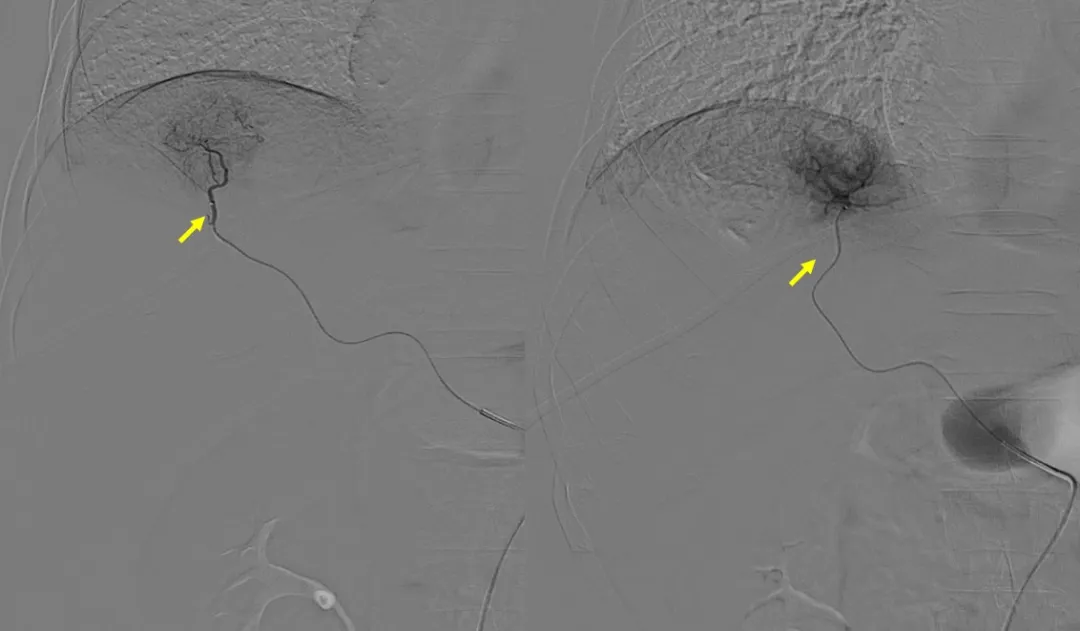
Tumor embolization with drug loaded microspheres (indicated by yellow arrow)
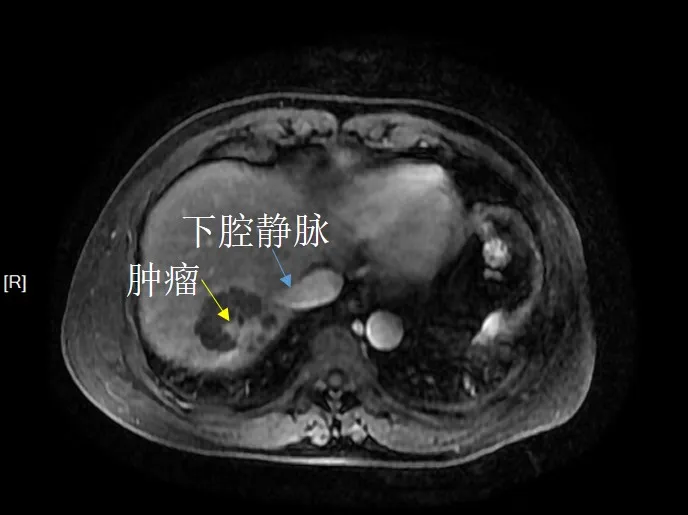
After embolization with drug loaded microspheres, the tumor active area shrank and the edge was further away from the inferior vena cava compared to before treatment
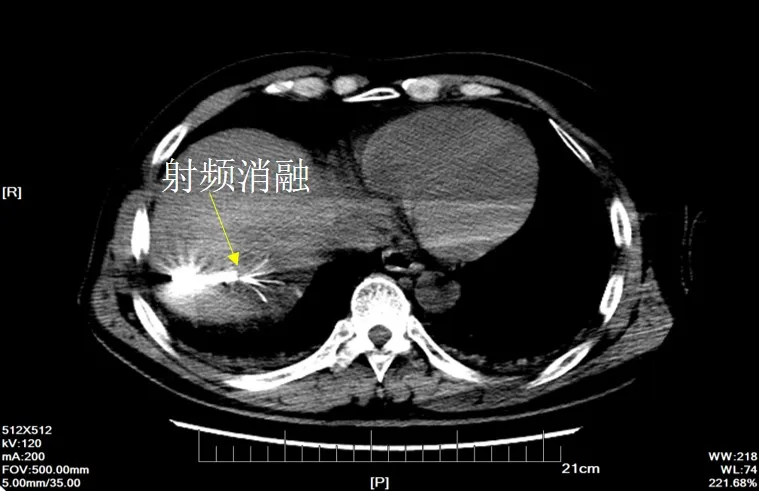
After evaluation by the medical team, percutaneous liver puncture radiofrequency ablation treatment was performed on the remaining tumor area under general anesthesia
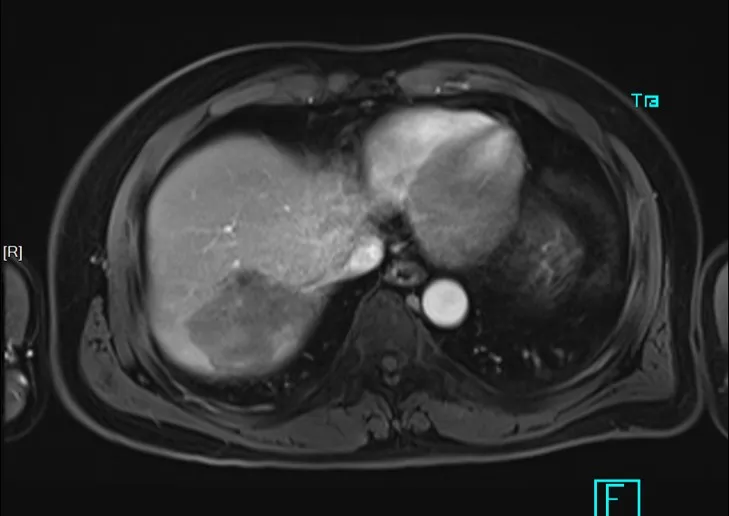
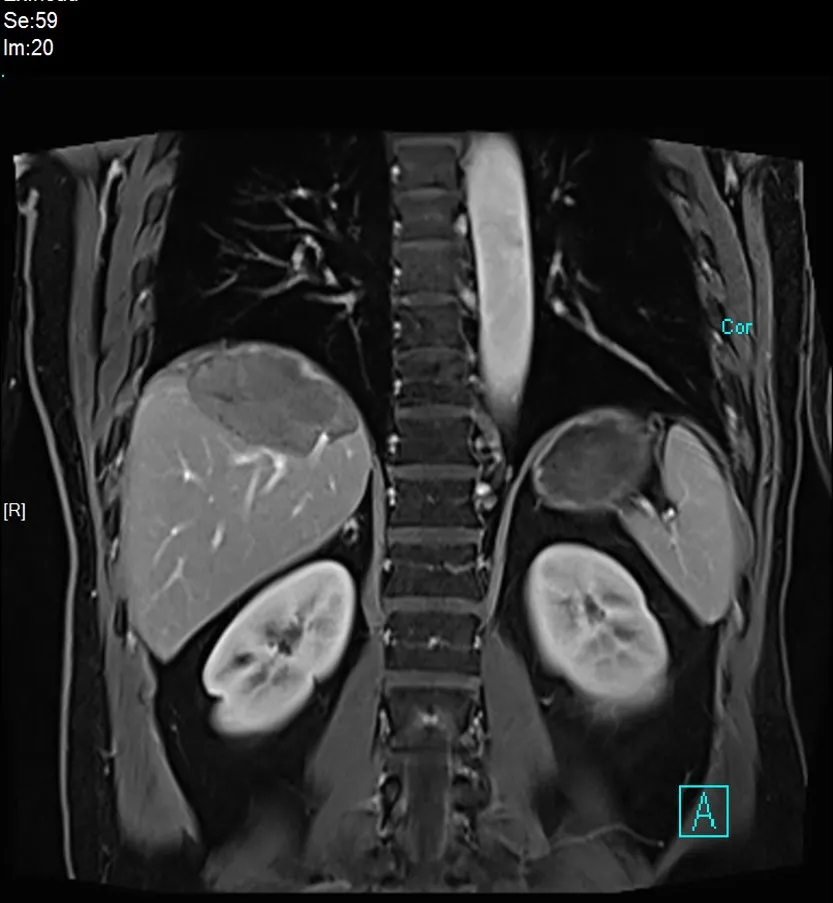
After 1 month of ablation, magnetic resonance imaging was re examined and the tumor was completely inactivated. The tumor marker AFP decreased to 1.7ng/ml.
This set of "combination fists" makes tumors "nowhere to hide"
Zheng Lin said that liver cancer is a common malignant tumor in China, and most liver cancer patients have a tumor diameter greater than 5 cm (known as large liver cancer) or multiple nodules, making surgical resection difficult.
Hepatic artery chemoembolization is an important non-surgical treatment for liver cancer, which can be achieved through minimally invasive intervention techniques, arterial superselective catheterization, precise delivery of chemotherapy drugs to the tumor area, and occlusion of tumor blood vessels to treat the tumor. It is divided into traditional iodinated oil embolization (c-TACE) and drug loaded microsphere embolization (DEB-TACE). However, chemotherapy embolization also has its shortcomings. Although this method can effectively shrink tumors, it is not easy to achieve radical cure.
Thermal ablation is a curative method for tumors, but due to the limitations of the ablation range, simple ablation treatment requires a tumor diameter of no more than 3 cm and no more than 3 tumors. So for large liver cancer, if surgery is not suitable, how can curative treatment be achieved? That is to first shrink the tumor through chemotherapy embolization, and then combine with thermal ablation for curative inactivation of residual active areas. A minimally invasive intervention "combination punch" allows the tumor to have nowhere to hide.
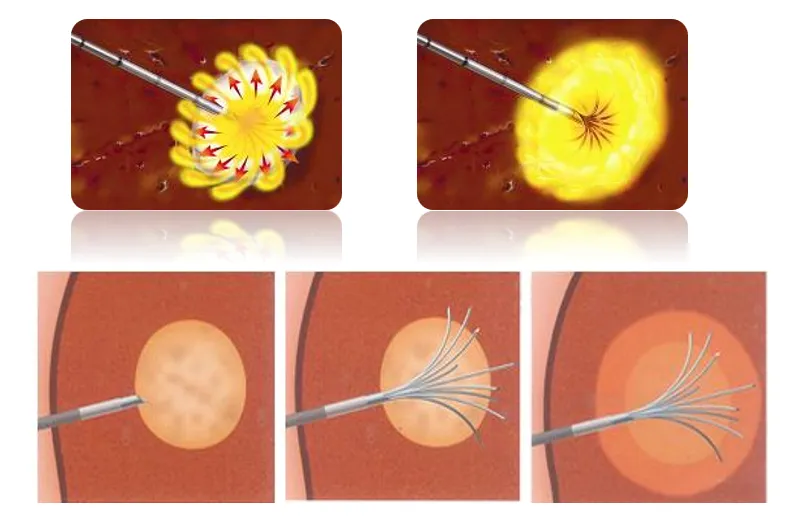
Type of ablation needle and ablation range (diameter 2-5 cm)
"Getting large liver cancer is actually not scary. Through minimally invasive intervention surgery - hepatic artery chemoembolization - the active area of the tumor can be reduced, and combined with thermal ablation, the remaining active part can be" forcefully chased and fiercely attacked "to achieve complete tumor inactivation." Zheng Lin said.
Hu Hongtao, Deputy Director of Minimally Invasive Intervention Department, said that in recent years, minimally invasive intervention therapy technology has developed rapidly, and the emergence of new liver cancer treatment weapons has further improved the effectiveness of liver cancer intervention therapy, highlighting the importance of intervention therapy in liver cancer treatment. In the future, the clinical application of Y90 radioactive embolic microspheres for nuclear weapons, the implementation of public welfare policies for centralized procurement of ablation equipment, and the clinical application of Kangbo knife, a cold and hot composite ablation device that can achieve a larger ablation range, will enable more patients who cannot undergo surgery to achieve radical treatment through minimally invasive intervention. The combination of intervention and surgery, through preoperative neoadjuvant or conversion therapy, can also provide more potential resectable liver cancer patients with the opportunity for surgical surgery.
This article is reprinted from "Dingxiangyuan"
Surgerycast
Shanghai Headquarter
Address: Room 201, 2121 Hongmei South Road, Minhang District, Shanghai
Tel: 400-888-5088
Email: surgerycast@qtct.com.cn
Beijing Office
Address: room 709, No.8, Qihang international phase III, No.16, Chenguang East Road, Fangshan District, Beijing
Tel: 13331082638( Liu )
Guangzhou Office
Address: No. 15, Longrui street, longguicheng, Taihe Town, Baiyun District, Guangzhou
Tel: 13302302667 ( Ding )